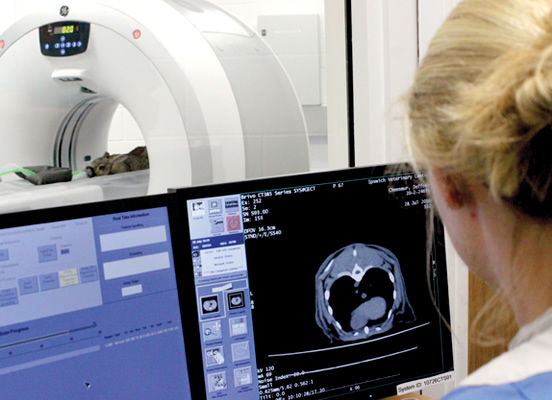
Our radiographer-led service provides high quality three-dimensional images. Our advanced imaging capabilities enable better diagnoses and can result in more effective treatment for animals.
CT uses radiation to take sliced images through the body. These slices are then grouped together using computer software and can be reconstructed to give us a three-dimensional image. Images are acquired quickly, resulting in a shorter anaesthetic time for the patient. Its speed makes the CT scanner a fantastic tool in trauma situations.
CT imaging is unparalleled at demonstrating bones, joints, soft tissue structures, organs and vessels. Contrast studies are carried out to better detect tumours, vasculature and the spinal cord.
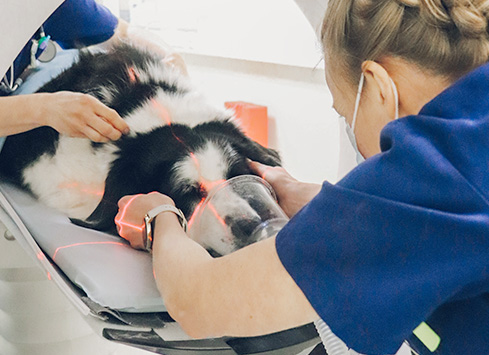
Common uses for CT scanning:
Tumour detection and metastatic screening
Tumours are often very vascular and appear clearly, following the insertion of contrast. Using contrast in combination with CT imaging, we can differentiate tumours from other soft tissue structures or cysts. If a primary cancer has been found and treated, CT can be used to monitor the spread of the tumour. Regular metastases scans can be performed, to ensure no reoccurrence.
Joint problems
CT provides detailed images of bones and joints. It is useful when diagnosing conditions such as hip and elbow dysplasia, limb deformities, bone necrosis, osteochondritis dissecans, arthritis and fractures.
Respiratory disorders
The lungs can be analysed in great detail using CT images. Due to the scanner’s thin slice capacity, small lung nodules can be detected, as well as other gross pathology, such as pneumonia and lung torsions.
Fractures
Images can be reconstructed into three dimensions, which can then be used to aid diagnosis or assist with surgical planning.
Trauma
Due to its speed, CT can be very useful in a trauma situation. It can detect fractures, haemorrhage, free air and traumatic foreign bodies.
CT-guided biopsies
For any hard-to-reach areas, biopsies can be performed under CT guidance.
CT angiograms
A CT angiogram is a contrast study that highlights the body’s vasculature. It can demonstrate anomalies, such as portosystemic shunts, thrombus and aneurysms.
CT myelograms
A CT myelogram involves contrast media being injected into the subarachnoid space in the spine. It is used to detect compression on the spinal cord, which is often caused by intervertebral disc disease, herniated disc material or tumours.
